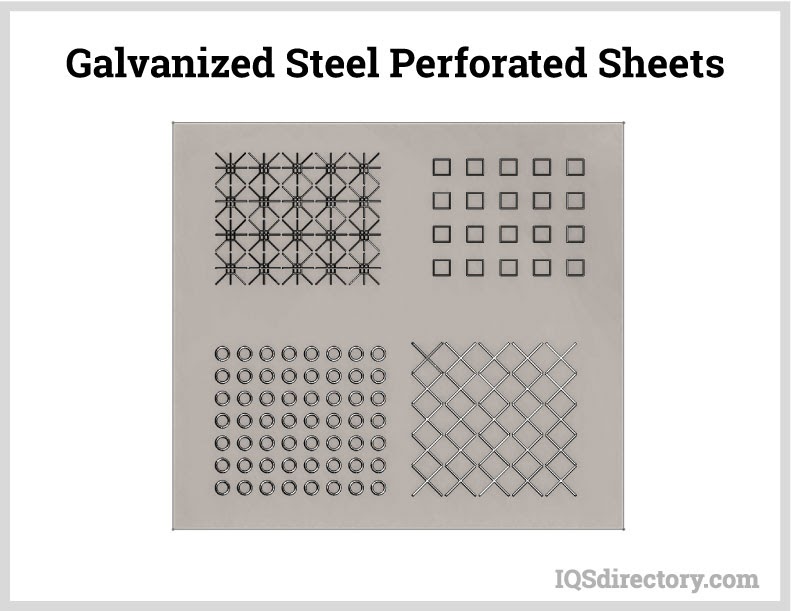
Perforated metals are a type of metal sheet that has been mechanically stamped or punched to create an array of holes, slots or decorative patterns. The process of creating perforated metals involves a mechanical press, which punches the holes or slots into the sheet. The size, shape, and spacing of the holes can be customized to meet specific needs and applications. Read More…
Accurate Perforating is a one-stop shop for complete perforated metal solutions. We can perforate, fabricate and finish almost any metal for almost any use. Whether you need perforated aluminum, carbon steel, galvanized, stainless steel, or copper; in perforated sheets, coils, parts or finished components; or architectural metal, decorative metal, railings, facades or sunscreens — with the...
Here at Remaly Manufacturing Company, Inc. we aim to exceed your expectations. Our teams utilize the most efficient manufacturing processes and we strive to provide you with the highest quality solutions. All of our products are pre-tested and we work with you to determine the best perforated metals for your applications.
Our commitment to excellence is reflected in the superior quality of our perforated metal products. We understand the diverse needs of our customers, and our extensive range of perforation patterns and materials ensures that we can meet and exceed expectations across various industries.

Here at VACCO Industries, we can create custom perforated metal products, and our engineers will abide to your exact requests. These top of the line products are affordable, and we work hard to make all of our products with precision techniques

More Perforated Metal Manufacturers
Perforated metals are a type of metal sheet that has been mechanically stamped or punched to create an array of holes, slots or decorative patterns. The process of creating perforated metals involves a mechanical press, which punches the holes or slots into the sheet. The size, shape, and spacing of the holes can be customized to meet specific needs and applications.
Perforated metals have a rich history, dating back to ancient times when craftsmen used punched metal designs to create decorative objects. The technique gained popularity during the Industrial Revolution when mass production methods allowed for the creation of perforated metal sheets in large quantities. Today, perforated metals are used in a wide range of applications.
Creation of Perforated Metals
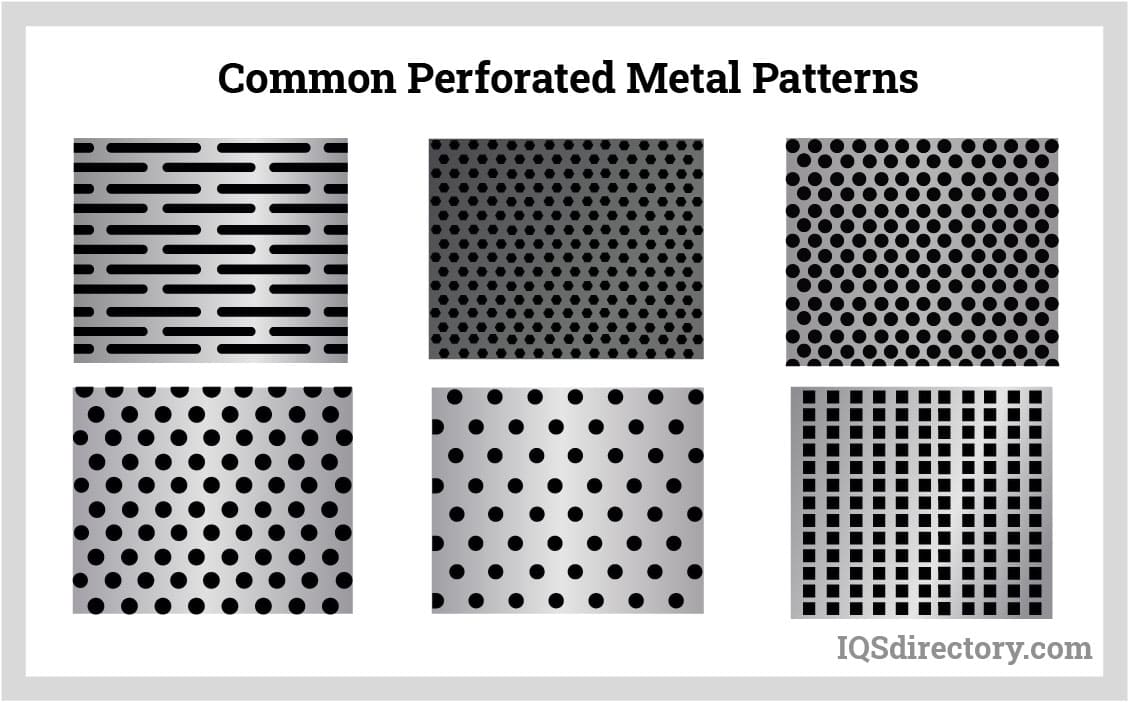
Perforated metals emerge through a diverse array of manufacturing techniques involving the stamping or punching of holes into metal sheets. Specialized machinery tailored for perforation plays a pivotal role in this process. Commonly fashioned from stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, or galvanized steel, these sheets offer unique properties and benefits. The perforations themselves can take on various forms: round, square, rectangular, slotted, or bespoke designs tailored to specific needs. Advanced methods like laser cutting or CNC machining further allow for intricate patterns and precise customization. These meticulous processes ensure consistent hole size, spacing, and overall quality in perforated metal sheets, making them indispensable across diverse industries such as architecture, construction, filtration, and beyond.
Types of Metals Used and Applications
Perforated metals derive their versatility from a spectrum of materials, each meticulously chosen for distinct virtues and uses. Stainless steel stands out for its robust defense against corrosion, formidable strength, and aesthetic allure, making it a favored option in architectural endeavors like facades, cladding, and interior embellishments. Aluminum, prized for its featherlight constitution, thrives in aerospace and automotive realms, as well as in ventilation systems and ornamental pursuits. Carbon steel, prized for its endurance and cost-efficiency, powers industrial machinery, construction gear, and agricultural tools. Galvanized steel, fortified by a zinc shield, excels in thwarting corrosion, proving indispensable in outdoor edifices, fencing, and agricultural domains. Each metal flaunts unique merits, catering to a gamut of industries with bespoke solutions.
Surface Finishes and Treatments for Perforated Metals
Surface finishes and treatments are pivotal in elevating the functionality, visual appeal, and longevity of perforated metals. These treatments cater to diverse requirements by applying various methods to the perforated metal sheets. One prevalent technique is powder coating, where a dry powder adheres electrostatically to the metal surface, later solidifying into a robust and decorative shield upon heat curing. This method excels in offering formidable resistance to corrosion, a spectrum of colors, and enduring durability, rendering it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Anodizing stands out as a favored treatment for aluminum perforated metals, entailing an electrochemical process that engenders a protective oxide layer on the surface. This not only fortifies against corrosion but also presents a gamut of decorative finishes and hues. Galvanizing, on the other hand, shields steel perforated metals by applying a zinc layer, thereby enhancing resilience against corrosion. For those seeking distinctive aesthetics or functional attributes, decorative plating is employed, involving a fine application of precious metals such as nickel, chrome, or brass.
By carefully selecting the optimal surface treatment, perforated metals can be tailored to precise design specifications and performance prerequisites. These treatments augment resistance against corrosion, abrasion, and environmental factors, thereby ensuring enhanced durability and visual appeal across various applications.
Limitations and Overcoming Challenges
Perforated metals, though versatile, come with inherent limitations, particularly concerning their structural robustness and susceptibility to deformation. The act of perforation compromises the material, diminishing its load-bearing capability. To counter this, manufacturers opt for thicker metal sheets, implement reinforcement methods like flanges or stiffeners, or utilize perforation patterns that evenly distribute stress across the sheet. These strategies safeguard the metal’s integrity while achieving the desired perforation effects.
Benefits of Perforated Metals
Perforated metals are prized across industries for their versatile advantages. Initially, they bolster airflow and ventilation, perfect for HVAC systems, air conditioners, acoustic panels, and speaker grilles. This capability enhances heat dissipation and air quality. Additionally, they offer clarity and structural robustness, making them ideal for security screens, partitions, and facades where visibility and aesthetics are crucial. Furthermore, they foster creative design, enabling aesthetically appealing architectural elements and decorative finishes indoors and out. Perforated metals serve multifaceted roles, acting as effective filters or screens that regulate the movement of liquids or gasses. This versatility proves indispensable across industries like oil and gas, food processing, and automotive, where exacting filtration and separation are critical. Moreover, perforated metals contribute to noise reduction when deployed as sound barriers or acoustic panels. Their advantages extend to enhancing airflow, visibility, design flexibility, filtration efficiency, and acoustic management. Consequently, perforated metals emerge as a dynamic solution, catering adeptly to diverse applications across various sectors.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Perforated Metals
Perforated metals embody significant sustainability advantages and make positive environmental contributions. Their recyclability stands out prominently: materials like stainless steel and aluminum, commonly used in perforated metals, are derived from recyclable sources, enabling reuse at the end of their lifecycle. This reduces reliance on fresh raw materials and curtails waste. Moreover, the manufacturing process itself is efficient, with minimal waste generated from hole punching that can be repurposed or recycled. Furthermore, perforated metals demonstrate commendable energy efficiency. By integrating perforated metal panels into building facades or shading structures, it becomes possible to regulate solar heat gain effectively, thereby decreasing reliance on artificial cooling and cutting down energy consumption. The perforations in metal panels enhance natural ventilation, diminishing the necessity for mechanical ventilation systems and promoting energy conservation. Additionally, incorporating perforated metals in architectural designs facilitates daylighting, harnessing natural light to reduce dependence on artificial lighting. Ultimately, perforated metals contribute to sustainability and environmental responsibility through recyclability, energy efficiency, waste reduction, and their capacity to support sustainable design principles, making them an ideal choice for eco-conscious projects.
Customization and Design Possibilities of Perforated Metals
Perforated metals unlock a realm of boundless creativity and adaptability, making them an ideal choice for architects, designers, and artists alike. Their design versatility springs from the ability to craft unique patterns of holes, ranging from simple geometric shapes to intricate, multifaceted designs. Tailoring options span hole size, shape, spacing, and open area, offering precise control over both visual aesthetics and functional characteristics. Designers can explore various densities of perforations to achieve desired levels of transparency, opacity, or privacy. Furthermore, perforated metals can be personalized to incorporate branding elements, logos, or artistic motifs, thereby establishing a distinct visual signature. With the evolution of computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) technologies, perforated metal sheets can now be meticulously crafted, enabling the realization of intricate designs that were previously daunting. The interplay of light and shadow through these perforations imbues facades, partitions, ceilings, and decorative elements with captivating depth and visual allure. Whether crafting architectural marvels, artistic installations, or practical interior design components, the customizable nature of perforated metals presents boundless avenues for creativity and self-expression.

Choosing the Correct Perforated Metal
Selecting the right perforated metal for a particular application demands meticulous evaluation of several factors. Initially, identifying the preferred hole pattern—comprising dimensions like shape, size, and spacing—is essential, aligning with both functional needs and aesthetic preferences. Subsequently, material choice assumes paramount importance, taking into account attributes such as corrosion resistance, strength, and longevity. Assessing the environmental conditions, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures, is crucial when selecting a metal that can endure its designated surroundings. Furthermore, it’s essential to evaluate the load-bearing capacity and structural demands to guarantee the chosen perforated metal can withstand anticipated stress levels and uphold its integrity. Moreover, seeking advice from perforated metal manufacturers or suppliers with diverse expertise can offer valuable insights and direction. They can help in selecting the suitable metal type, thickness, perforation design, and finish to ensure optimal performance and durability for the intended use. Considering these factors enables one to select the ideal perforated metal that fulfills both functional and aesthetic needs, ensuring superior performance in the chosen application.
Applications of Perforated Metals
Perforated metals find diverse applications across various industries. In architecture and construction, they serve as ornamental panels, sunshades, and building facades. Within industrial manufacturing, they play crucial roles in filtration, separation, and drying operations. In transportation, perforated metals are essential for grilles and ventilation systems, while in the food industry, they function as baking trays or screens. Their adaptability makes perforated metals highly favored among designers and engineers alike.
Stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and carbon steel are among the commonly perforated metal types. Each of these metals possesses unique qualities that render them suitable for perforation. Below, we delve into the specific applications of each of these perforated metals.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is favored for perforated metals because of its exceptional resistance to corrosion, durability, and capability to retain shape and strength even in harsh conditions. It finds widespread application in industries like food processing, chemical processing, and architecture.
Aluminum: Aluminum, prized for its lightness and malleability, stands as an exceptional material for tasks demanding adaptability. Its versatility finds frequent application in transportation, construction, and aerospace sectors.

Copper: Copper’s exceptional conductivity and superb thermal properties render it a favored option in electrical and heat transfer domains. Its distinctive appearance also makes it sought after for decorative purposes.

Brass: Brass, a copper alloy prized for its robustness, resistance to corrosion, and distinctive sheen, finds frequent application in decorative arts, plumbing, and electrical installations.
Carbon Steel: Carbon steel, renowned for its robustness and longevity, proves indispensable in industrial realms like filtration, separation, and drying processes. It also finds widespread application in architectural projects.
The Future of Perforated Metal
The future of perforated metals holds promise for exciting developments and advancements. A pivotal area of potential progress involves leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing or additive manufacturing. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize perforated metal production, enabling the creation of intricate and complex designs that were once challenging to achieve. With the capability to meticulously craft perforation patterns, a realm of potential unfolds for distinctive architectural facades, ornamental features, and practical uses. Furthermore, progress in material science might yield innovative alloys or coatings, promising heightened corrosion resistance, superior strength-to-weight ratios, and optimized performance tailored to diverse environments. Perforated metals have the potential to broaden their application across various industries and uses. Additionally, amid increasing emphasis on sustainability, there is a rising curiosity about eco-friendly and recyclable materials for perforated metals, thus promoting more sustainable manufacturing approaches. The future of perforated metals promises a landscape shaped by innovation, technological leaps forward, and an expanded array of applications. This evolution presents thrilling prospects for designers, engineers, and manufacturers to explore the limitless possibilities of this versatile material.
Choosing the Proper Perforated Metal Manufacturer
To maximize your chances of a successful purchase of perforated metal from a manufacturer, it’s crucial to compare multiple companies listed in our directory of perforated metal manufacturers for the best outcome. Every perforated metal manufacturer features a detailed business profile showcasing their expertise and capabilities. Explore each company’s specialization quickly using our patented website previewer. Contact manufacturers directly through our streamlined RFQ form to gather information or request quotes from multiple companies effortlessly.
Check out our Wire Mesh website
Check out our Metal Stampings website




 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting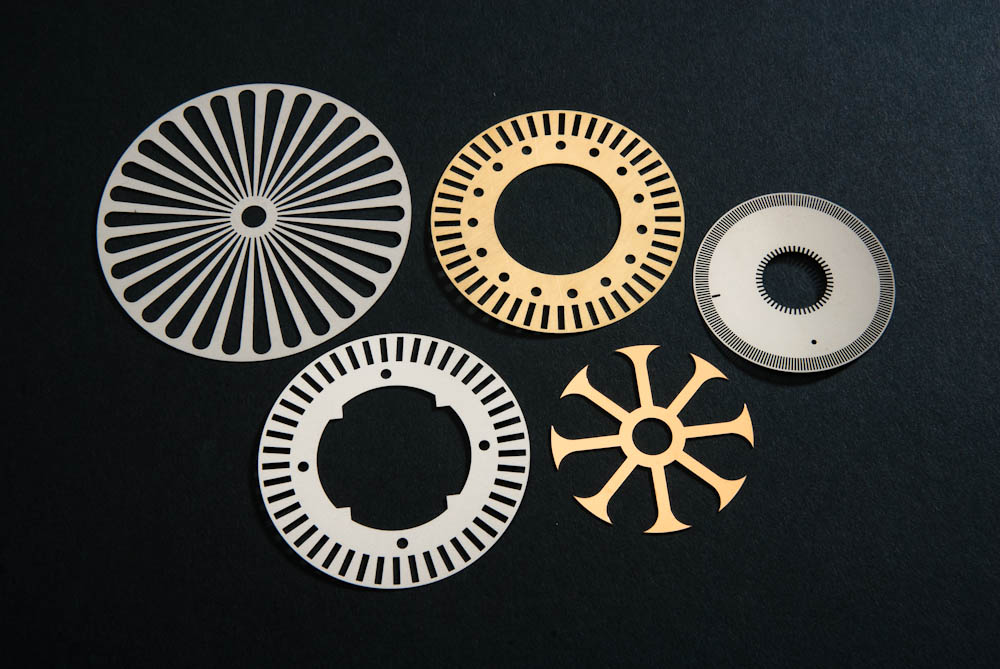 Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication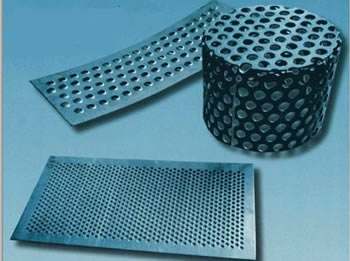 Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services